Phishing and Spoofing
Phishing
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack often used to steal user data, including login credentials and credit card numbers. It occurs when an attacker, masquerading as a trusted entity, dupes a victim into opening an email, instant message, or text message.
It is also the attempt to acquire sensitive information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details, often for malicious reasons, by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communications.
EXAMPLE:
An email from PayPal arrives telling the victim that their account has been compromised and will be deactivated unless they confirm their credit card details. The link in the phishing email takes the victim to a fake PayPal website and the stolen credit card information is used to commit further crimes.
Spoofing
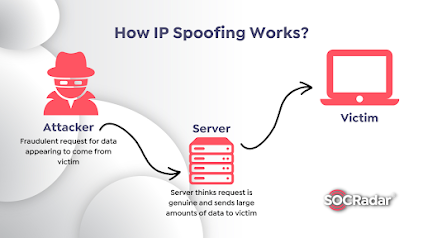
A common spoofing scenario happens when an email is sent from a fake sender address, asking the recipient to provide sensitive data. Typically, the recipient is prompted to click on a link to log into their account and update personal and financial details.
Attack is when a malicious party impersonate another device or user on network hosts, steal data, spread malware or bypass access controls.
EXAMPLE:
This is the most common type of spoofing attack where the victim is targeted using email communication. The sender looks like a trusted source with an email address that closely resembles the original address.
References:
https://www.investopedia.com/terms/s/spoofing.asp#:~:text=What%20Is%20an%20Example%20of,update%20personal%20and%20financial%20details. (Example of Spoofing)
https://www.imperva.com/learn/application-security/phishing-attack-scam/ (Phishing meaning)

.jpg)

Comments
Post a Comment